ACTIVITIES AND PROCESS
HWE members run a wide range of processes for recycling, recovery and disposal of hazardous waste:
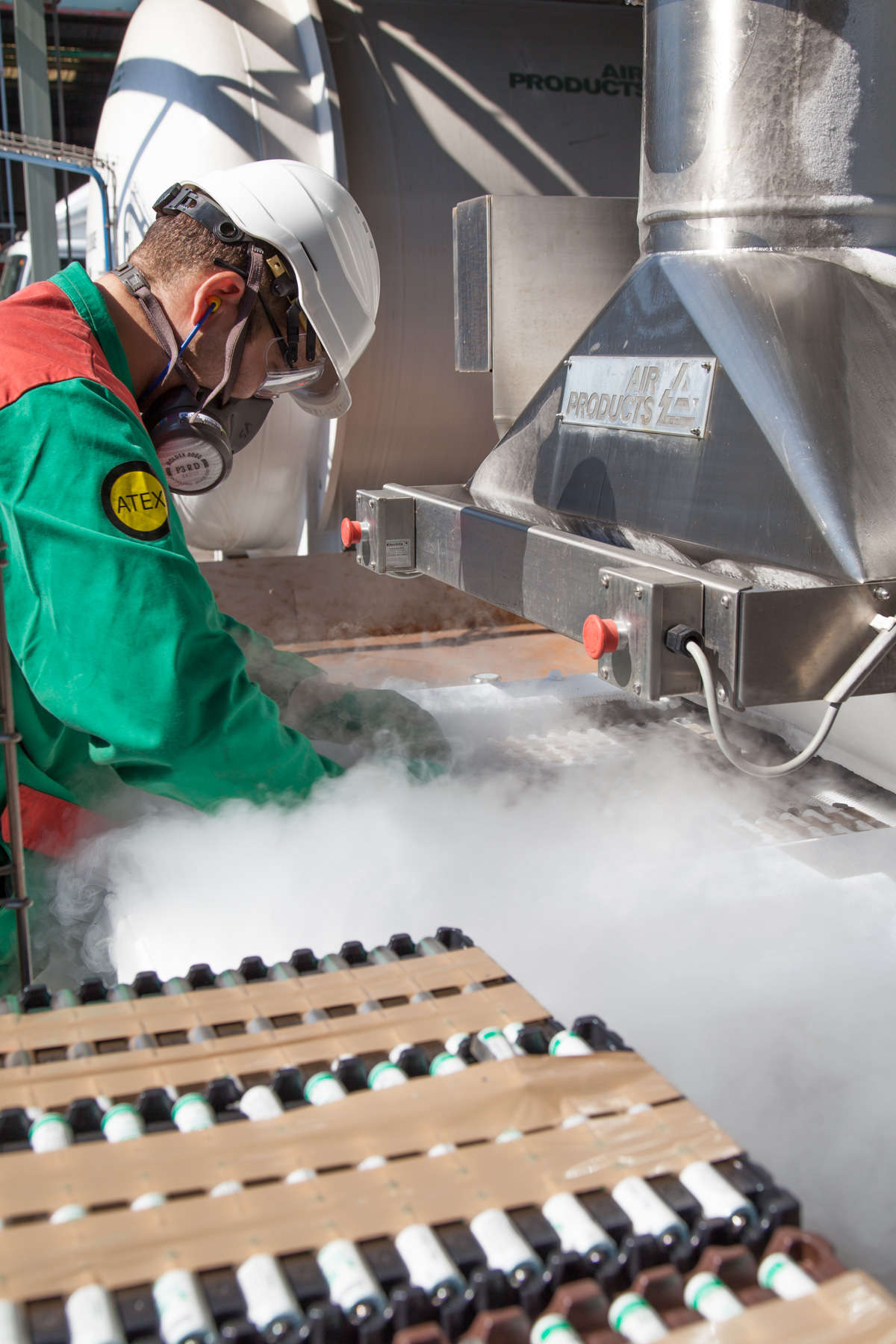

→ Regeneration of solvents, mineral oils, chromic baths, fuels
→ Water recycling
→ Recovery of metals by pyrometallurgical and hydrometallurgical processes
→ Recovery of other materials (soils, plastics, scrap metals, …)
→ Energy recovery
→ Physico-chemical treatments
→ Biological treatments
→ Incineration – evapo-incineration – evapo-concentration
→ Management and treatment of PCBs
→ Landfill


EU legislation with regards to Endocrine Disruptor: HWE’s view
In the framework of the fitness check of the EU rules regarding harmful chemicals, HWE answered the stakeholder's consultation on endocrine disruptors. The adoption of a comprehensive and integrated framework on endocrine disruptors, common criteria to define them...

New Circular Economy Action Plan: HWE position
Following the publication of the European Green Deal (https://ec.europa.eu/info/files/communication-european-green-deal_en), the EU Commission is consulting stakeholders on its new Circular Economy Action Plan. ...

HWE participated in the 2019 Triple COPs in Geneva
The 2019 Triple COPs took place in Geneva from the 29th of April to the 10th of May. Governments from across the world have converged on Geneva this week for discussions and decisions aiming at protecting human health and the environment from chemicals and waste. The...

HWE present at the COP2 of the Minamata Convention
The Minamata Convention on mercury intered into force in August 2017 The second meeting of the Conference of the Parties (COP2) took place from 19 to 23 November 2018 in Geneva, Switzerland. The Convention, whose Secretariat is based in Geneva, aims at “protecting the...

Application of EU legislation on Hazardous Waste: European Member States can do better
Bound to oversee the proper application of the EU legislation, the EU Commission mandated the consulting firm BIPRO in 2014 to assess the implementation of hazardous waste management in EU Member States. A first study published in 2015 concluded that most requirements...

WSR consultation – HWE in favour of holding on the basic principles
The Waste Shipment Regulation (WSR, 1013/2006) establishes procedures and control regimes for the shipment of waste, depending on the origin, destination and route of the shipment, the type of waste shipped and the type of treatment to be applied to the waste at its...

8 European professional associations advise against a hasty use of the BATAELs given in the draft incineration BREF
The professional associations CEWEP http://www.cewep.eu/, ESWET http://www.eswet.eu/, FEAD, MWE, Euroheat & Power https://www.euroheat.org/, EURITS http://www.eurits.org/, HWE and CEFIC http://www.cefic.org/ advise against a hasty use of the emission and energy...

Hazardous waste Europe’s answer on the communication & staff working document on the implementation of the circular economy package
The promotion of non-toxic material cycles in the discussions on circular economy is of utmost importance for Hazardous Waste Europe, not only to protect consumer’s health and encourage efficient use of resources, but also to enhance the value of recovered materials,...

HWE joins the UN pledge towards a pollution free planet
We are deeply convinced that only a model built on non-toxic materials cycles can and will ensure a safe and sustainable circular economy. To reach this ultimate goal, we are committed to strive that substances or materials streams contaminated with toxic substances...
Hazardous Waste Management situation in 14 EU countries
A few months ago, willing to support the provisions of the waste framework directive dealing with hazardous waste management, the EU Commission requested the consultant BIPRO to assess the hazardous waste management situation in 14 Member States, with a special focus...
HWE members are present throughout the entire hazardous waste treatment chain. Thus, after collecting the waste, they characterise it in order to provide the most appropriate treatment for the protection of the environment and health. Two solutions are therefore envisaged :
→ if it is technically and economically feasible to decontaminate the hazardous waste, then it is recycled and the extracted hazardous substances are disposed of in accordance with environmental regulations
→ if it is not technically and economically feasible to decontaminate the hazardous waste, then it is disposed of entirely, in order to prevent the release of the hazardous substances it contains into the environment or into the recycled products.
